Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
鈴木 賢治*; 三浦 靖史*; 城 鮎美*; 豊川 秀訓*; 佐治 超爾*; 諸岡 聡; 菖蒲 敬久
no journal, ,
The beam of synchrotron X-rays has the advantage that it can be so small, and we can make detailed stress maps using the X-ray beam. However, it is difficult to measure residual stresses of a welded part due to a dendritic structure. This difficulty is caused by the difference in the positions of the diffracted crystal grains. To solve this problem, we proposed a double exposure method (DEM). In this presentation, the DEM was applied to measuring the residual stress of the plate which was cut from the welded pipe. The detailed stress maps under a biaxial stress state were obtained. On the other hand, the residual stress distributions of the welded pipe under a triaxial stress state. From these results, the detailed stress maps of the root part of the butt-welded pipe were made up by the complimentary use of the synchrotron X-rays and neutrons. The results can significantly explain the initiation and propagation of SCCs. We name this analysis method the quantum beam hybrid stress analysis.
Zhang, Y.*; 梅田 岳昌*; 諸岡 聡; 宮本 吾郎*; 古原 忠*
no journal, ,
Essential understanding of the pearlite growth kinetics is of great significance to predict the lamellar spacing and the resultant mechanical properties of pearlitic steels. In this study, a series of eutectoid steels with Mn addition up to 2mass% were isothermally transformed at a temperature range from 873K to 973K to investigate the growth kinetics and the underlying thermodynamics at the migrating interface during pearlite transformation. The microscopic observation revealed that the pearlite growth rate in each alloy becomes increased while the lamellar spacing becomes decreased by lowering the transformation temperature. Mn addition decelerates the growth rate, accompanied by a relatively wider lamellar spacing at each temperature. After analyzing the element distribution in the vicinity of migrating austenite/pearlite interface via three-dimensional atom probe, Mn was found to be enriched at the austenite/pearlitic ferrite interface, whereas the Mn partitioning among the three phases is negligibly small in the 2mass% Mn added alloy isothermally transformed at 873K. Based on the estimation of energy dissipated by various factors, the driving force for pearlite transformation in the Mn-free alloy was found to be consumed by interface friction, carbon partitioning and ferrite/cementite interfacial energy, whereas neutron diffraction analysis indicated that the influence of transformation strain is relatively small. The retardation effects of pearlite growth kinetics in the Mn-added alloy, which is partly due to the reduced driving force for pearlite transformation, can be well explained by further considering the energy dissipation caused by solute drag effects of Mn.
都留 智仁; Lobzenko, I.
no journal, ,
ハイエントロピー合金(HEA)は、その優れた機械的・熱力学的特性から注目されている。特に体心立方構造(BCC)を有するHEAの一部は高強度と伸びのバランスに優れた特徴や特定の元素を含むBCC-HEAが特異なすべり痕を生じることが知られている。しかし、これらの特性の発現機構は十分に解明されていない。HEAの優れた機械的特性のメカニズムを解明するためには、構成元素の影響を考慮した欠陥構造の原子レベルの描像を理解することが不可欠である。転位構造と転位運動が、HEAの機械的特性を特徴づけるため、VNbMoTaWとTiZrNbHfTaの2種類のBCC HEAに対する転位の挙動の違いについて考察することが有効である。本研究では、第一原理計算を用いてBCC HEAの転位芯構造の検討を行った。その結果、TiZrNbHfTaの平均二乗原子変位は非常に大きく、構成元素である第IV族元素がそれに大きく寄与することがわかった。また、HEAにおける転位のダイナミクスを捉えるための新しい手法を開発した。
Lobzenko, I.; 椎原 良典*; 森 英喜*; 松中 大介*; 都留 智仁
no journal, ,
近年、機械学習が材料科学に広く応用されている。原子シミュレーションの分野においても、人工ニューラルネットワークによる原子間ポテンシャル(ANNポテンシャル)の構築が行われるように、第一原理計算と近い精度で、材料の様々な特性を再現することが示されている。本研究では、材料の重要な特性の一つである原子応力に着目した。原子応力は古典的な近似で計算できる。また、微視的な応力の解析は、あらゆるタイプの不均一系(バルク、二次元結晶、分子集合体などの欠陥など)に適用できる。我々は、原子応力テンソルを導出するために、ANNポテンシャルのフレームワークで中心力分解(CFD)スキームの応用を他の方法と比較して検討した。CFDを用いない方法では、応力テンソルの対称性が崩れる可能性があるため、正しい応力テンソルを記述するためにはCFDを使用する必要があることがわかった。この原子応力の応用問題として、さまざまな方位を持つ純粋なAlの表面付近の原子応力分布を評価した。第一原理研究から、Al表面付近で電荷振動が存在することが知られている。この特徴は、既存の原子間ポテンシャルでは捉えることが困難であったが、ANNポテンシャルを使用して得られた結果は、Al表面付近の原子応力の振動を正しく再現することが確認された。我々のポテンシャルはAl構造のエネルギーのみ(量子力学近似で計算)を出力するが、原子応力振動は実際の系の電荷分布を反映している。
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 相澤 一也; 山崎 倫昭*
no journal, ,
An in situ neutron diffraction experiment during cyclic tension-compression with an applied strain of  0.01 and was conducted at room temperature using a Mg
0.01 and was conducted at room temperature using a Mg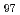 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy, after hot-extrusion at 723 K with the extrusion ratio of 10, to understand the deformation behavior of both
alloy, after hot-extrusion at 723 K with the extrusion ratio of 10, to understand the deformation behavior of both  Mg and LPSO phases and to elucidate kinking in the LPSO phase including its effect to the strength during the cyclic tension-compression deformation. The evolutions of textures, lattice strains of individual constituent phases measured from neutron diffraction will be plotted with the applied stress, strain and the cyclic number, and details will be presented in this presentation.
Mg and LPSO phases and to elucidate kinking in the LPSO phase including its effect to the strength during the cyclic tension-compression deformation. The evolutions of textures, lattice strains of individual constituent phases measured from neutron diffraction will be plotted with the applied stress, strain and the cyclic number, and details will be presented in this presentation.
Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.; Mao, W.
no journal, ,
Applications in aerospace, linear motors, and other fields have created a need for superior structural materials at cryogenic temperatures. In response, it has become necessary not only to develop structural materials with excellent mechanical properties at cryogenic temperatures, but also to investigate the cryogenic deformation mechanism of such materials. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a method to observe microstructures including the phase stresses during cryogenic deformation. To answer this question, we have developed a cryogenic horizontal deformation tester and an in-situ measurement method during cryogenic deformation on the neutron diffractometer TAKUMI installed at the high intensity pulsed neutron facility, J-PARC. We have also already obtained several excellent results from the in situ measurements during cryogenic deformation, which will be presented in this presentation.